Adaptive Health Behavior Inventory (AHBI)
The Adaptive Health Behavior Inventory (AHBI) is a powerful and versatile assessment of intrinsically motivated adaptive health behaviors, goal-directed actions, health habits, and beliefs that adult's develop in response to different but common health-related social demands. These intrinsically motivated adaptive behaviors represent an adult's preferences, likes, dislikes, and perceptions of their own physical capabilities as they interact with and respond to the health-related demands arising from themselves or their environment.
- The Adaptive Health Behavior Inventory (AHBI) is a 20 item assessment
- Likert-item response scale
- Average time to complete the AHBI is four minutes.
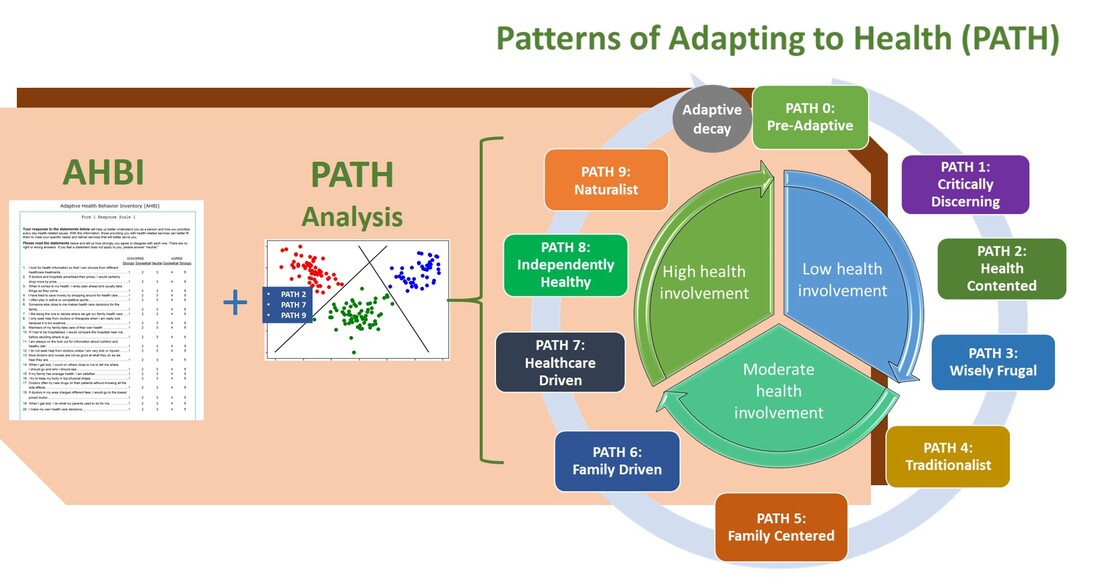
AHBI + path Analysis
When paired with PATH Analysis, adult responses to the Adaptive Health Behavior Inventory (AHBI) detect the level of conformity to each of the nine patterns of adapting to health (PATH) and assign that person his or her dominant PATH, or identify the person as in the Pre-Adaptive stage, or the stage of Adaptive Decay.
Adaptive Health behavior inventory (AHBI)
Predictive validity examples
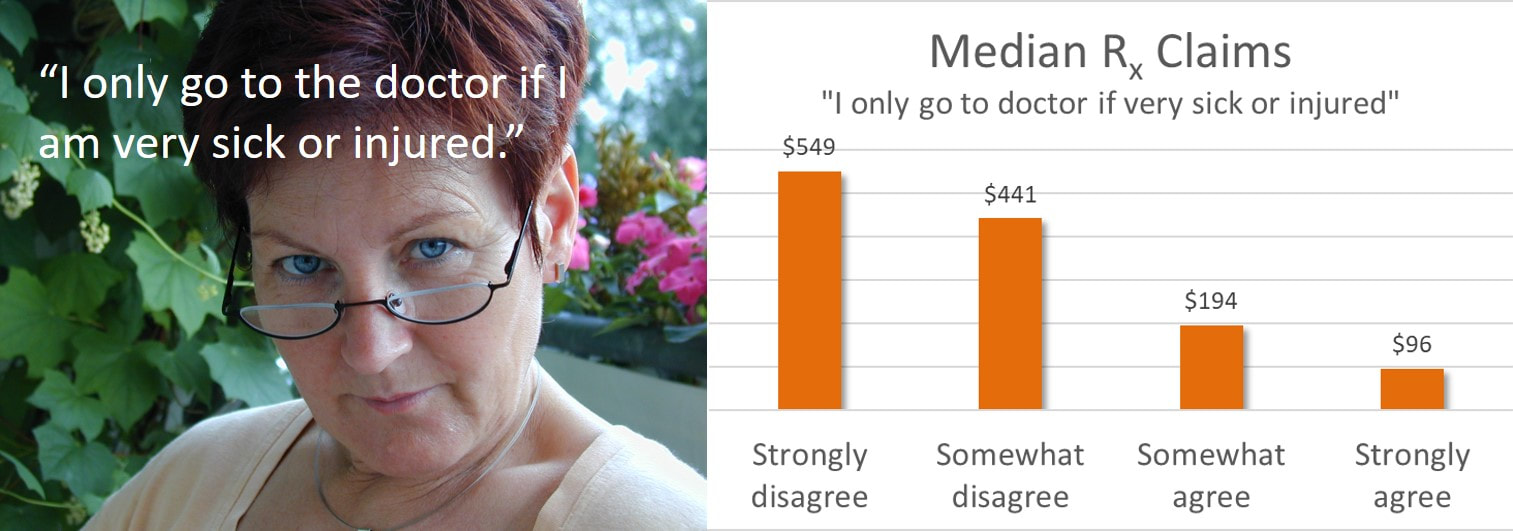
AHBI Measures: Care Seeking in Response to Perceived Illness and Medical Expenditures
Medical claims levels across AHBI measures of "care seeking in response to perceived illness" support their relationship to actual behavior. Responses indicating a delay of health care seeking have been associated with reduced medical expenditures associated with physician visits and use of prescription medications.
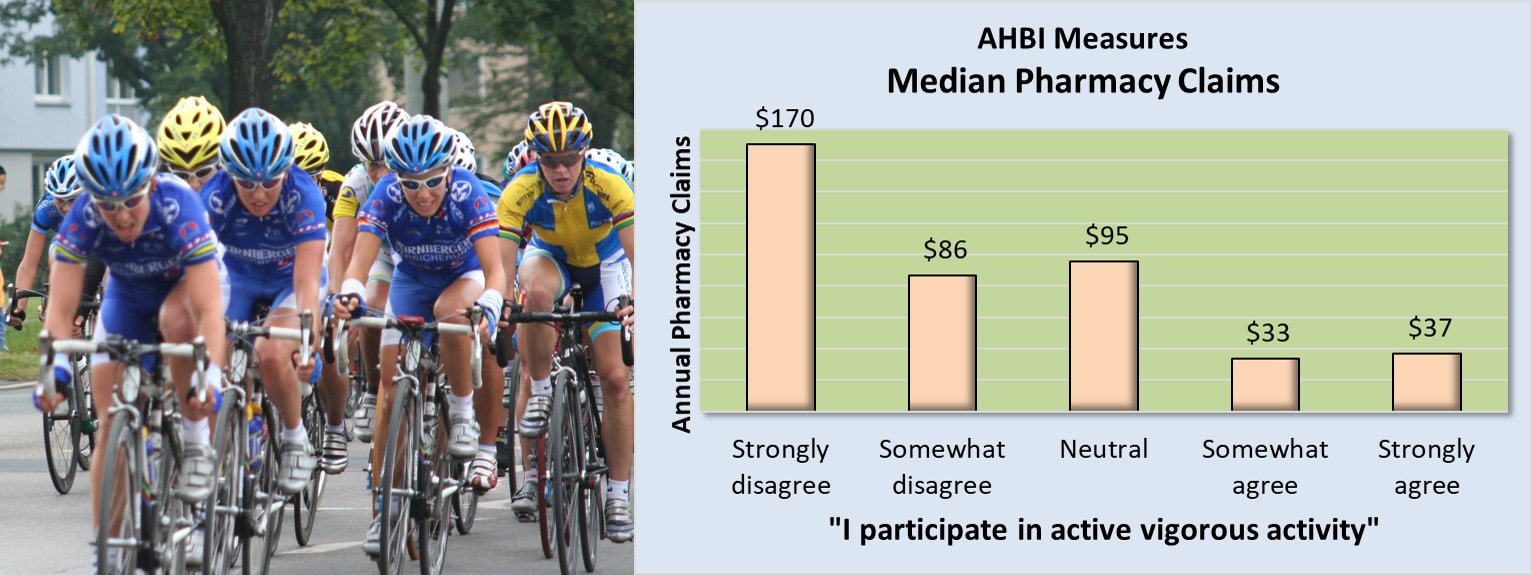
AHBI Measures: Vigorous Physical Activity and Medical Expenditures
Pharmacy claims levels associated with response patterns to AHBI measures of "vigorous physical activity" support their association with both the need and freedom from prescription medications. Those adults who describe themselves as regularly engaging in active vigorous exercise generate lower demand for prescription medications compared to adults who don't.
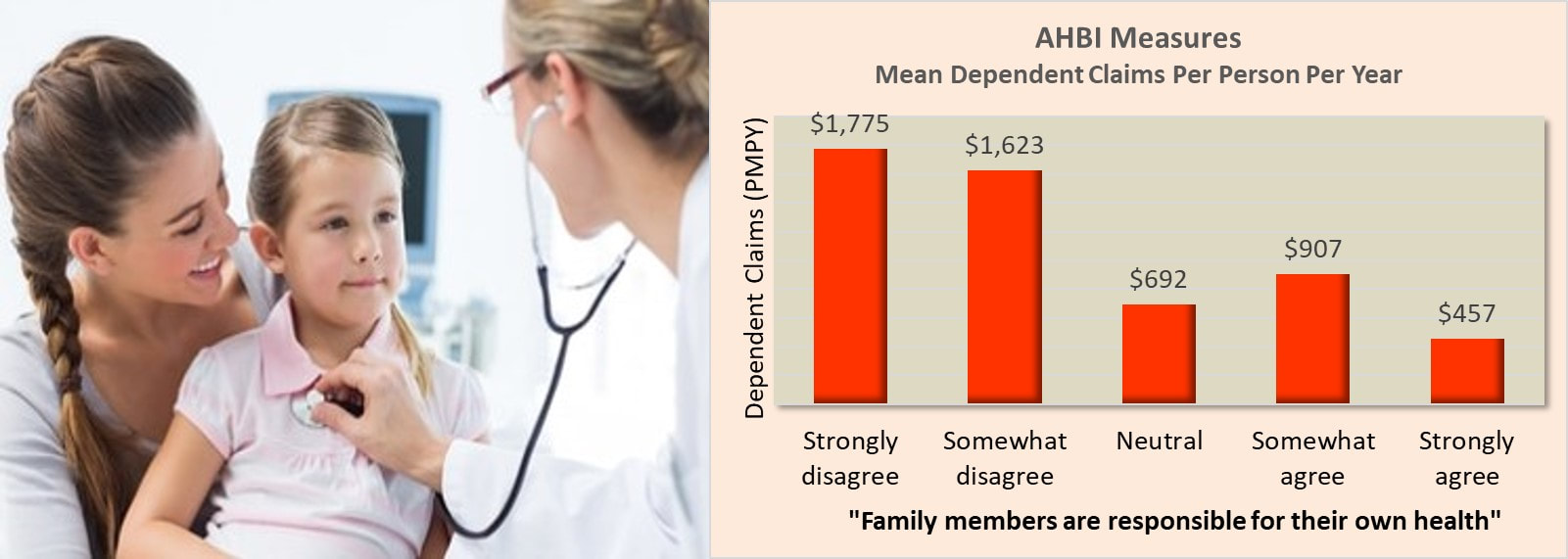
AHBI Measures: Responsibility for Family Health and Dependent Claims
Dependent medical claims levels across response patterns to AHBI measures of "responsibility for family health" support their association with both higher (strong disagreement) and lower (strong agreement) seeking of medical care for dependents.
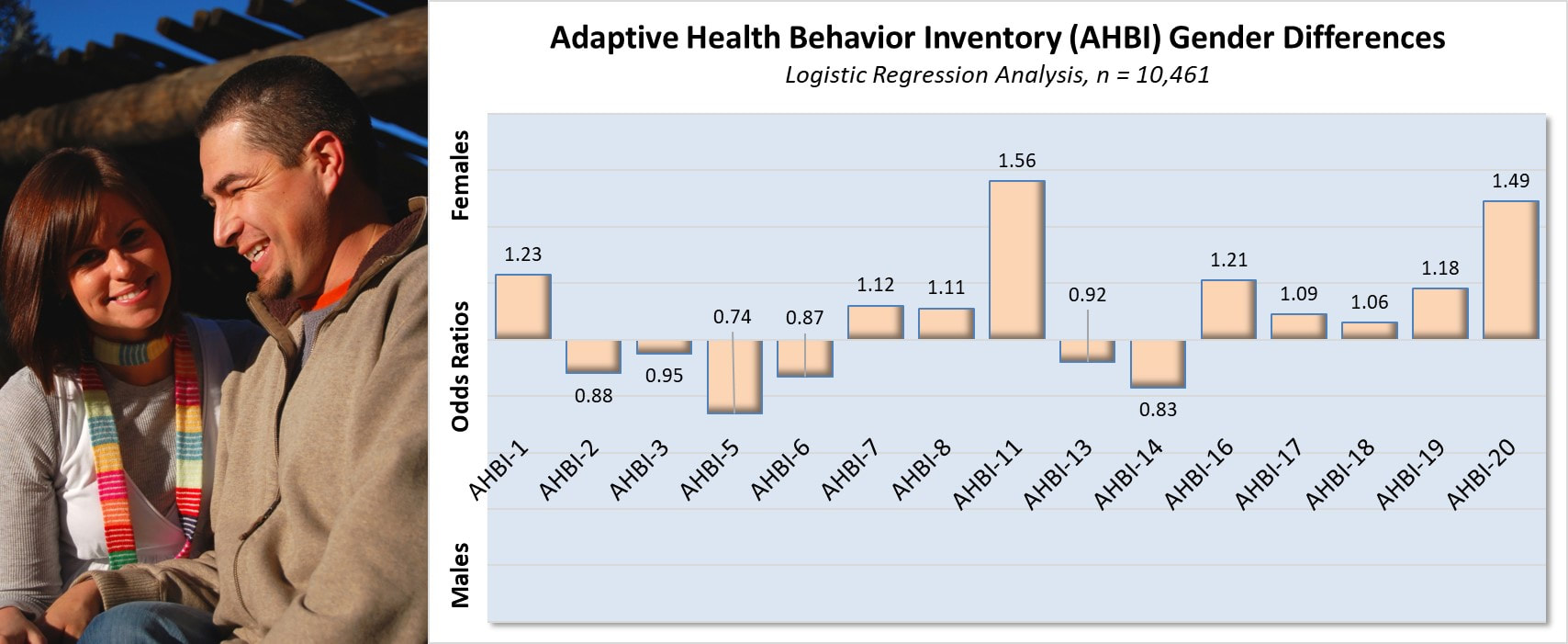
AHBI Measures: Health-Related Behavior Gender Differences
Fifteen of the 20 AHBI measures discriminate between women and men and identify gender-based differences in health-related behaviors, particularly in relation to seeking information about nutrition (AHBI-11) and internal locus of health decision-making responsibility (LofHDR) (AHBI-20).
Adaptive health behavior inventory (AHBI) Content
|
AHBI is a language-based psychometric assessment designed to assess multiple health-related dimensions of response to different health contexts. The health dimensions confirmed by factor analytic studies include:
Applying the AHBI The AHBI is appropriate for any adult population within the U.S. The AHBI has also been successfully used in the United Kingdom and China. The AHBI can be applied as a stand-alone assessment or integrated into a larger assessment or questionnaire. |